Hazardous Waste Storage, Associated Risks and Disposal
If you have stored hazardous waste in your premises, voluntarily or involuntarily, this article is for you.
Hazardous waste is generated at both the industrial and household levels.
Industrial hazardous waste includes materials such as:
- Toluene and Benzene
- Water ink solvent
- Heavy metal solutions
- Electronic scrap
- Waste battery
- Paint waste
Household hazardous waste includes:
- Lamp ballasts
- Drain cleaners
- Motor oil
- Pesticides
- Medical wastes
- Discarded electronics
Faraway nuclear plants aren’t the only places that produce hazardous waste that's collected by people wearing hazmat suits. In reality, hazardous waste is far more commonplace than you might think.
If you store the hazardous waste safely, and follow EPA’s regulatory guidelines, you can avoid major risks, and do a great service to the nearby communities and the environment.
How to Store Hazardous Waste
The possession of hazardous waste makes you responsible for the safety of people and the environment around you.
Hazardous waste shows one or more these four different qualities in varying degrees:
- Toxicity (paint waste, motor oil)
- Flammability (solvent-based paint waste, waste kerosene)
- Corrosivity (rust removers, battery acid)
- Reactivity (waste concentrated bleaches, pressurized aerosol cans)
1. Storage
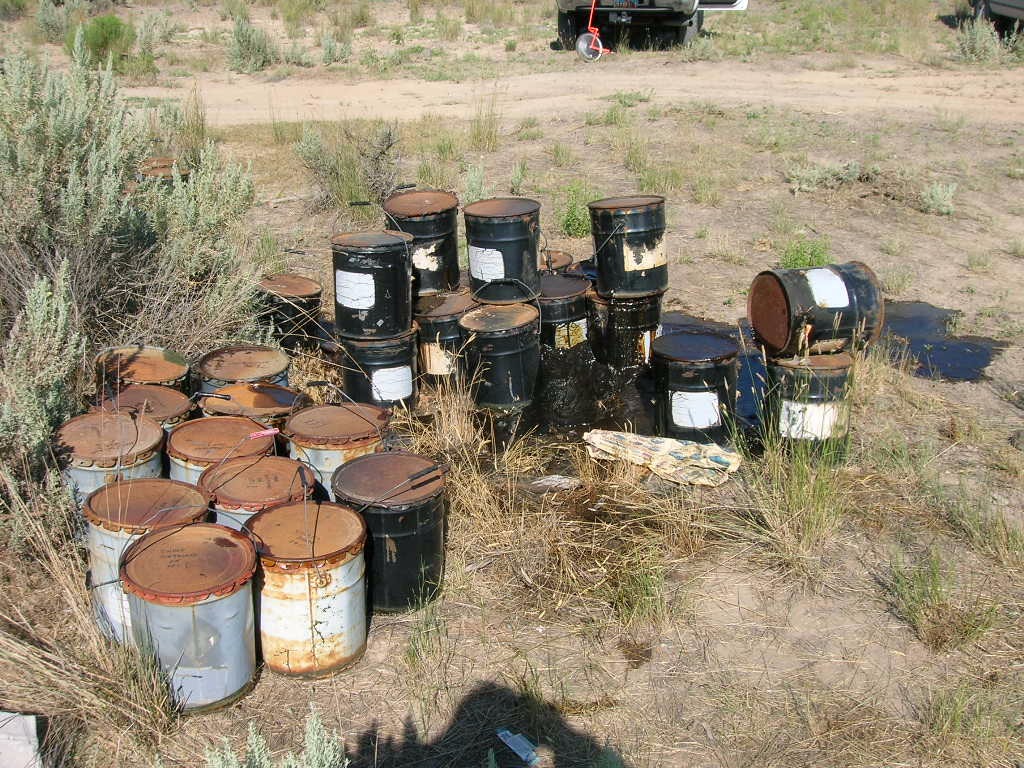
Your first responsibility is to buy suitable storage to hold these wastes safely. These include:
- Containers
To store hazardous waste, containers must meet regulatory requirements such as being free from cracks and gaps, having a sloped base to facilitate drainage of liquid waste, being compatible with the hazardous wastes, etc.
Examples of containers include 55-gallon drums, tanker trucks, railroad cars, buckets, test tubes, etc.
- Tanks
You can move containers from place to place, but tanks are stationary. The regulations for tanks mandate that tanks must have adequate structural support, corrosion protection, presence of a secondary containment system, etc.
Other methods of hazardous waste storage include containment buildings, landfills, injection wells, and surface impoundments.
2. Labelling
Practice labelling your containers, as it will reduce your and the waste management company's work. The first requirement is to clearly mark "Hazardous Waste" on each container. The label must include the name and a description of the waste. Also record the date the accumulation begins and the name and address of the waste generator.
According to 40 CFR 262.16(b), hazardous waste should not be accumulated for more than 180 days, and the quantity of accumulation should not exceed 6,000 kg.
If you don't have a way to dispose of, recycle, or treat hazardous waste, contact a waste management company to take care of it. Enviro Care provides its waste management services across the US.
Risks Associated with Hazardous Waste Storage
1. Fire, Explosion, and Accidents
The generation and storage of hazardous waste is a high-risk activity. It's a danger for those who knowingly or unknowingly come into the vicinity of the waste.
Leakage of reactive waste like sodium and cyanide wastes, ethers, peroxides, pyrophoric can cause an instant explosion upon contact with air or water.
Hazardous waste leaks and spills pose a serious threat to property and are a physical hazard.
You can read this report by EPA on emergency incidents related to hazardous waste.
Routine checkups and investment in proper storage can minimize the risks associated with hazardous waste storage.
2. Passing Inspection Tests
The EPA conducts routine inspections every 2-5 years (the frequency is based on the size of the facility and waste generation). OSHA conducts inspections without prior notice.
Both of these authorities are responsible for enforcing health and safety requirements at the workplace. Their ultimate motive is to reduce the chances of accidents and injury in and around the facility.
Hazardous waste generators must adhere to specific regulations. Different waste generation facilities need to follow different regulations such as:
- Acquiring an EPA ID Number
- Conforming to on-site accumulation limits
- Disposing of, treating, or handing over the waste to a waste-management company before the time limit
- Having trained personnel
- Having holdings that meet certain specifications
Not abiding by these regulations can result in fines and penalties. The EPA's fine for hazardous waste violation can be up to $93,750. OSHA penalties can amount to as much as $13,494 for serious violations.
Incurring penalties can cause both financial setbacks and reputational damage.
3. Health Hazards
Leaked hazardous waste poses a serious health hazard to humans and wildlife. The risk of direct and indirect contact with waste makes precautionary measures and following regulations all the more necessary.
When they are burned, reactive wastes produce gases that cause respiratory diseases, eye inflammation, etc. Corrosive waste attacks living tissues and inflicts damage on contact. Toxic waste can impair the functioning of the nervous system and cause dizziness, confusion, vomiting, etc.
Coming into contact with hazardous waste can cause:
- Cancer
- Genetic mutation
- Physical deformation
- Reproductive impairment
- Behavioural abnormalities
Contact with leaked hazardous waste can also kill humans and wildlife.
How to Dispose of Hazardous Waste
There are several methods for disposing of, treating, and recycling hazardous waste. But some of them require you to set-up a facility of your own, which can be costly.
Hazardous waste is treated chemically, thermally, biologically, or physically. Methods include ion exchange, oxidation, incineration, landfarming, filtration, sedimentation, etc.
If the waste can't be treated, it's stored in landfills and underground injection wells.
If you produce hazardous waste, store it safely and hand it off to a waste management company once a sufficient amount of waste accumulates.
Hiring a waste management company will make your hazardous waste tasks significantly easier, as they train their personnel to handle such tasks. They bring their specialized tools and ensure the safety of people on the site. Hiring a waste management company shows your customers you care about the environment and believe in sustainable business practices.
Contact us for Hazardous Waste Management, Transportation and Disposal
Enviro Care offers nationwide waste management, transportation, and disposal services. Our methods are environmentally friendly, and we implement programs that will benefit your business in the long run.
Local, state, and federal agencies trust us to manage their waste. We also offer a 24-hour emergency response service, and our fleet of trucks and trailers and our trained staff is always ready to work.
Do you have hazardous waste lying around at your facility? Contact us today!